Local Elections Herald a New Era For The AKP
Publication: Eurasia Daily Monitor Volume: 6 Issue: 61
By:
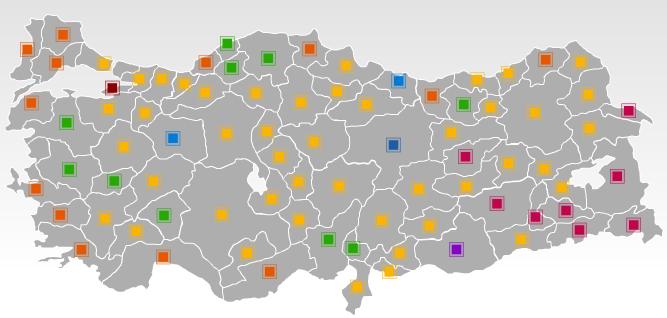
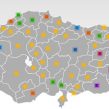
Turkey’s local elections on March 29 produced mixed results, with the governing Justice and Development Party (AKP) emerging victorious, yet underperforming compared with earlier elections. The AKP received a 38.86 percent share of the vote, while the Republican People’s Party (CHP) and the Nationalist Action Party (MHP) gained 23.10 and 16.08 percent respectively. The AKP’s support fell from 46.6 percent in the 2007 general elections and 41.7 percent in 2004 local elections (www.ntvmsnbc.com.tr, March 30). While retaining its popularity within major cities, it failed to further expand this and lost several mayoral posts. The gains made by opposition parties raise the specter of imminent changes in Turkish politics.
Prime Minister Recep Tayyip Erdogan, acknowledging his party’s losses, emphasized that the AKP did not fall below its performance in the local elections in 2004. It received almost the total percentage of votes cast for its two rival parties (www.cnnturk.com, March 29). The representatives of the opposition parties, in contrast, referred to their increases in the share of the vote, and the "erosion" of the incumbent party’s popular support.
The results exposed wide regional variations and followed an apparent trend in previous elections: whereas the AKP controlled central Anatolia, the CHP and MHP were popular in the Aegean and Mediterranean coastal provinces as well as in the northwestern provinces in the Thrace region. Significantly, the MHP regained some of its past strength in central Anatolia, challenging the AKP’s dominance over center-right voters. In addition to the defeat it suffered vis-à-vis the pro-Kurdish Democratic Society Party (DTP) in the southeastern provinces, the AKP’s support also declined in some northern regions. The Islamist Felicity Party (SP), an alternative to the AKP for some conservative voters, also increased its vote to 5.17 percent.
The local elections marked the first decline in the AKP’s share of the vote since the general elections in 2002. Despite surpassing its major rivals by a clear margin, the psychological effect of this decline is undeniable. Previously, the party claimed to be the only viable choice for the electorate. However, a series of electoral victories arguably bred a sense of overconfidence, which left the AKP in general, and Erdogan in particular, open to accusations that they have grown insensitive to criticism, either from society or opposition parties, and developed an authoritarian style of leadership. Faced with losing popular support, the AKP will likely soften its discourse, and foster compromise with the opposition.
Turkish opposition parties, however, are now seeking to capitalize on the AKP’s apparently declining support, claiming that it has entered a period of rapid decay (www.ntvmsnbc.com.tr, March 29). Whether such drastic erosion is occurring remains to be seen, but the results may force the AKP to reconsider its policies. Indeed, Erdogan expressed dissatisfaction with the polls and admitted that the AKP must assess the causes of its decline. Meanwhile, he is expected to reshuffle his cabinet, possibly replacing some high-profile ministers involved in preparing the AKP’s discredited election strategy (www.cnnturk.com, March 29; www.ensonhaber.com, March 30). The AKP will also need to reevaluate its economic policies as well as the Kurdish question and the pursuit of political reforms.
Thus far, the government has ignored charges that the Turkish economy has been badly impacted by the global financial crisis. Although some of the AKP’s populist policies helped cushion the full effects of the crisis, economic considerations played a major role in the local elections. Particularly, the declining performance of the AKP in the Marmara, Aegean, and Thrace regions, as well as some Anatolian cities, reflected the impact of the crisis in Turkey’s industrial heartlands. In this context, the AKP will come under intense pressure to secure a loan from the IMF which it has tried to avoid, consequently leaving the country in a weaker bargaining position than before.
Moreover, the results represent a blow to the image of the AKP as an inclusive party, representing not only conservative Turks and Kurds but also liberal and secular voters. There appear to be limits to the AKP’s appeal to the Turkish people. Its failure to gain support within the western coastal provinces and in the Thrace region, and the traditionally less conservative central Anatolia, shows that the AKP has been unable to diversify its appeal. The DTP’s strong performance in the southeastern provinces is a setback for the AKP’s policies on the Kurdish issue. It shows that "identity politics" remains on the popular agenda, and the AKP’s policy of providing services and socioeconomic incentives alone cannot resolve the Kurdish problem. Crucially, the higher profile of the DTP suggests it cannot be ignored as a major stakeholder in any resolution of the Kurdish problem. Paradoxically, the AKP’s initiatives on the Kurdish issue, though failing to satisfy Kurdish voters, alienated some Turkish voters in the west, in turn boosting the MHP’s popularity.
The AKP has been a largely populist party, attracting votes from across the political spectrum. Since it is potentially losing ground to its rivals, it will come under pressure to address the deeper causes of these failures, or risk the further erosion of its popular support. Whether it can formulate consistent policies to address these multiple challenges, particularly over the looming economic crisis, will be an immediate and major test for the AKP’s government.